2016年11月9日,化学化工学院付宏刚教授领导的科研团队在Elsevier出版的《Applied Catalysis B: Environmental》上发表了题为“Sequential two-step hydrothermal growth of MoS2/CdS core-shell heterojunctions for efficient visible light-driven photocatalytic H2 evolution”的研究论文。
利用可见光分解水产氢是目前光催化领域的研究热点之一。构建有效的异质结构能够有效地提高半导体的光催化产氢性能。本文中,通过连续两步水热路线成功制备了核壳结构的MoS2-CdS催化剂。第一步水热过程中制备得到了花状的MoS2,随后向冷却的MoS2溶液中直接加入醋酸镉溶液进行第二步水热反应,在第二步水热反应中Cd2+与溶液中剩余的S2-以及MoS2中的S2-反应生成CdS,从而得到MoS2为核CdS为壳的核壳结构。通过改变Mo与Cd的摩尔比可以对复合结构中CdS壳层的厚度以及CdS的形貌进行调控。由于CdS在复合结构的外侧,因此有利于可见光的吸收且CdS与MoS2紧密接触形成有效的异质结促进了光生载流子的迁移,因此MoS2-CdS催化剂表现出了优异的可见光光催化产氢性能,20mg催化剂在可见光照射下无贵金属Pt的情况下产氢量能达到775 µmol·h-1远远高于纯的CdS(12 µmol·h-1)以及Pt-CdS(64 µmol·h-1)。
该项研究得到国家自然科学基金重点项目(21631004)的支持。论文第一作者为博士生吴爱平。
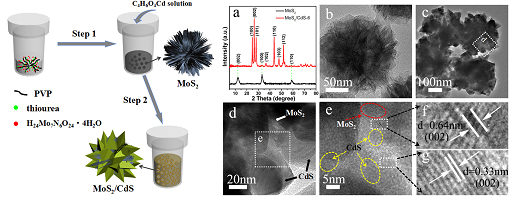
An easy and effective “sequential two-step hydrothermal growth” route has been developed for the construction of the core-shell structured MoS2/CdS hybrids with tunable micro-structure. The MoS2/CdS photocatalyst showed high catalytic activity (775 µmol·h-1, 20 mg catalyst, about 15.5 mmol h-1 g-1) and improved stability for PHE under visible light irradiation (λ> 420 nm). The good activity should be related with CdS outside shell beneficial for light adsorption and intimate contact of CdS and MoS2 for easy charge transfer.
Applied Catalysis B: Environmental上发表了题为“Sequential two-step hydrothermal growth of MoS2/CdS core-shell heterojunctions for efficient visible light-driven photocatalytic H2 evolution”. Appl. Cataly. B: Environ., 2017, 203, 955-963. 文献链接:http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0926337316308670